- Departments/Doctors
- Medical Services
- Inpatient Services
- Emergency Medical Services
- Issuance Services
-
Hemodialysis Center
- Specialized Centers
- Emergency Medical Center
- Cancer Center
- Cardio·Vascular Center
- Neuro·Vascular Center
- Cardio·Cerebro·Vascular Intervention Center
- Spine Center
- Joint Center
- Rehabilitation Center
- Laparoscopic Surgery Center
- Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Center
- Hemodialysis Center
- Home Nursing Center
- Comprehensive Health Examination Center
- Referral Center
- International Healthcare Center
Hemodialysis
This is one of renal replacement therapy for end-stage renal disease patients, in which the patient's blood comes out of the body through a special tube, and after wastes and water are filtered through a filter (dialysis machine), is injected back into the body. For the standard hemodialysis, it takes 4 hours at a time, 3 times a week for 12 hours a week, and the time can be adjusted according to the patient's condition.
Principles of hemodialysis
The principle of hemodialysis is as follows. With a semipermeable membrane as a boundary, the patient's blood with accumulated wastes on one side and the dialysate with a composition similar to that of a normal person's extracellular fluid on the other side flow in opposite directions. Then, the solutes including urea and other wastes accumulated in the blood are removed by diffusion due to the difference in concentration. And it filters the plasma by creating a difference in hydrostatic pressure to remove excess water in the plasma.
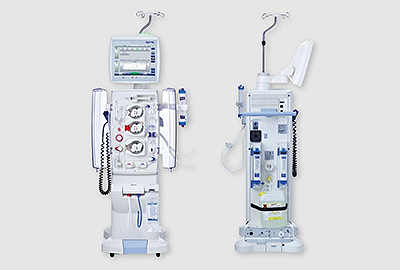
Hemodialysis
| Function | Contents |
|---|---|
| Toxin removal | It removes the wastes excreted by the kidneys. |
| Water removal | Removes unnecessary excess water to be excreted in the urine. |
| Electrolyte control | If there are excessive electrolytes in the blood such as sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, they are excreted using dialysis fluid, and if insufficient, they are supplemented with dialysis fluid. |
| Blood oxygen control | Acid is removed from the blood so that the blood becomes slightly alkaline, which is a normal state, or alkali is replenished through dialysate, which achieves acid-base equilibrium. |
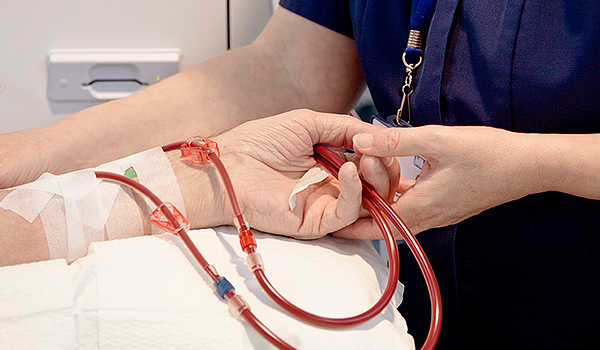
Vascular access
For hemodialysis, you need a vascular access through which the patient's blood can be drawn around 300ml per minute. This is called an arteriovenous fistula, which requires surgery several months before starting hemodialysis. However, if there is no vascular access at the time of hemodialysis, a hemodialysis tube is inserted into the jugular vein passing around the neck to perform dialysis. Therefore, patients who are being treated for chronic kidney disease need to consult with a nephrologist to prepare renal replacement therapy, and when necessary, they are referred to a surgeon for arteriovenous fistula formation.
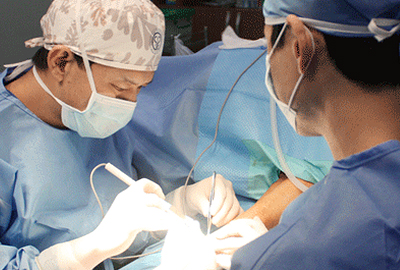
| Arteriovenous fistula (AVF) |
Arteries and veins are connected in arms and legs, etc. through simple surgery to make blood vessels thicker, which is most ideal for hemodialysis and can be used 1-2 months after surgery. |
|---|---|
| Arteriovenous graft | If blood vessels are not good, the arteries and veins are connected with an artificial tube made with a special material. It has a higher risk of occlusion than arteriovenous fistulas and can be used 2-4 weeks after surgery. |
| Catheter | For temporary purposes, it is used until the blood vessels grow after emergency or vascular surgery. A hemodialysis tube is inserted into a vein in your neck or chest. It can be used immediately after insertion and there may be a risk of infection. |
Once the vascular access is completed, the nurse will insert two needles into the vascular access at the start of each dialysis if it is an arteriovenous fistula or prosthetic. This needle is connected to the hemodialyzer through a soft tube. Blood is cleared from the dialysis membrane through one tube and sent back into the body through another tube. In case of a catheter, it is directly connected to the dialysis tube instead of using a needle.