- Departments/Doctors
- Medical Services
- Inpatient Services
- Emergency Medical Services
- Issuance Services
Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction Clinic
At the Angina and Myocardial Infarction Clinic, Shihwa Medical Center, equipped with up-to-date testing equipment, Cardiovascular Medicine Specialists with extensive clinical experience perform various tests for accurate diagnosis and systematic treatment of ischemic heart diseases such as angina and myocardial infarction, to protect your health in the heart and blood vessels.
What is ischemic heart disease?
There are several blood vessels called coronary arteries on the surface of the heart that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscles that are constantly working.
When this area of the coronary arteries narrows and the blood supply the heart needs is hampered, symptoms of pain or discomfort occur. Smoking, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and high blood pressure are obvious risk factors, while there are other factors such as physical activity that increase the body's oxygen consumption, obesity, and stress.
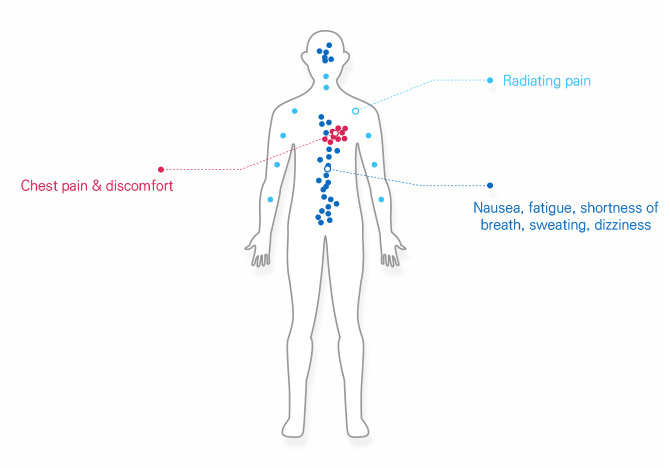
Main symptoms of ischemic heart disease
The main symptoms of angina include chest pain or chest discomfort. It mainly feels like a tight pressure or crushing pain in the back of the center of the chest, and although complaints vary from patient to patient, what’s common among them is the severe pain that can be felt in the chest. Sometimes the pain can be felt radiating to the shoulder, neck, jaw, arm, or back (radiation pain), and may be accompanied by nausea, fatigue, shortness of breath, sweating, or dizziness.
Classification of ischemic heart disease
-

Stable angina Stable angina that mainly appears during exercise lasts about 2 to 3 minutes, and chest pain disappears at rest. The reason chest pain gets worse during exercise is that, although the heart muscle needs more blood during exercise, the narrowed blood vessels do not provide adequate blood supply to the heart muscle, resulting in ischemic muscle. In particular, you may have more chest pain when exposed to cold weather or immediately after eating, even with the same amount of exercise.
-
Unstable angina In unstable angina, chest pain occurs unpredictably even at rest. Unstable angina should be suspected if chest discomfort is typical, but more severe and lasts longer than its first symptoms. It occurs when arteriosclerosis causes narrowing of coronary arteries or abnormal constriction of blood vessels, leading to decreased blood supply to the heart muscle. Unstable angina can also be caused by infection or inflammatory disease, which is one of the acute coronary artery syndromes that require emergency treatment.
-
Variant angina This chest pain occurs when the coronary arteries constrict due to spasms, etc. Chest pain usually occurs during night sleep or early morning and is often fine during daytime activities. It may cause myocardial infarction or sudden death, so caution is required.
-
Acute myocardial infarction When a coronary artery is blocked by a blood clot, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle is interrupted, resulting in necrotic heart muscle. As a result, the pressing or tightening pain in the middle of the chest lasts for 30 minutes. Chest pain may spread to the neck, jaw, shoulder, and left arm, pale complexion may occur, body temperature may drop, and cold sweat may occur.
Treatment of ischemic heart disease
Depending on the severity of the disease, one of the following treatment methods is selected: lifestyle changes, drug treatment, coronary intervention, and coronary artery bypass surgery.
01.
Drug treatment
The basic principle is to dilate the narrowed coronary arteries and relieve the burden on the heart. It is difficult to expect that drug treatment will lead to re-opening the blood vessels that are severely narrowed by arteriosclerosis. However, it can relieve the work of your heart muscle to reduce the frequency or severity of angina to some extent. Nevertheless, even when the chest pain decreases or disappears after drug treatment, it could be a bigger problem to think the disease is completely gone. Typical drugs for the treatment of angina include aspirin, which inhibits vasodilation and clot formation, lipid-lowering drugs that lower cholesterol in the blood, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
02.
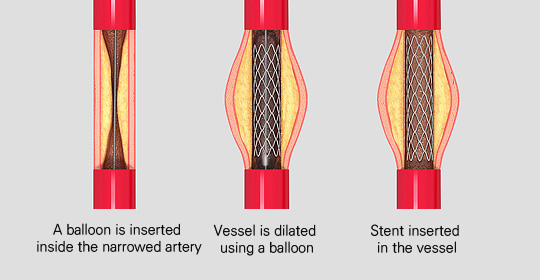
Percutaneous coronary intervention
Percutaneous coronary intervention refers to coronary angioplasty or coronary stenting. In this intervention, a tube is inserted into the coronary artery and the blocked blood vessel is expanded with a balloon or stent using a thin wire. Unlike surgery, it does not require anesthesia, recovery period is short, and it leaves no scars. Thus, it has been the largest part of angina treatment in recent years.
03.
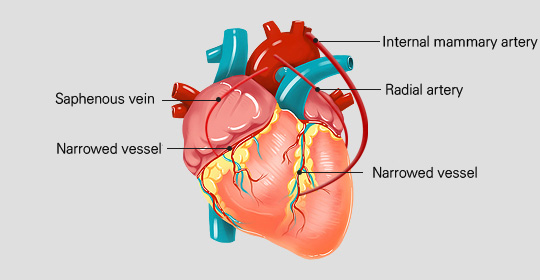
Coronary artery bypass surgery
In case angina is too severe to treat with percutaneous coronary intervention, coronary artery bypass surgery is used. In this surgery, the severely blocked part of the coronary artery is bypassed and a blood vessel is attached to the lower part of the narrowed artery using the internal mammary artery of the chest, the radial artery of the arm, or the saphenous vein of the leg.
Prevention of ischemic heart disease
The most important thing to prevent angina or myocardial infarction is to prevent its main cause, arteriosclerosis.
To that end, if the risk factors for arteriosclerosis, such as smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and cholesterol, are well managed, the incidence can be significantly reduced.
-
- Diet
-
- Eat a small amount of food frequently.
- Use vegetable oil for cooking
- Limit salt intake to l ess than 5g per day.
- Limit caffeine intake as it stimulates the heart.
- Eat a fiber-rich diet such as fresh vegetables, fruits, grains, and brown rice.
- People with high blood cholesterol levels take lipid-lowering drugs.
- Limit intake of foods high in cholesterol to no more than 3 servings per week. (egg, fish, meat offal, shrimp, eel, etc.)
-
- Exercise
-
- Warm-up for 3 minutes before exercise.
- Do aerobic exercise such as walking, jogging, and swimming.
- Do it for at least 30 minutes at a time, and do it consistently at least 3 days a week.
- Excessive and strenuous physical exercise should be avoided.
-
- Other
-
- Maintain an appropriate weight.
- Chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes must be steadily managed.
- It is recommended to avoid excessive stress over a long period of time if possible.
- Smoking is a factor that constricts blood vessels and obstructs blood circulation, so smoking should be stopped.