- Departments/Doctors
- Medical Services
- Inpatient Services
- Emergency Medical Services
- Issuance Services
Articular Rheumatism Clinic
Here at Articular Rheumatism Clinic, Shihwa Medical Center, we provide accurate diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, a typical autoimmune disease, gout, ankylosing spondylitis, Behcet's disease, ankylosing spondylitis, and lupus and appropriate medical treatment for each patient, as well as prevention of complications and sequelae. We provide the best medical service through continuous research and introduction of cutting-edge testing methods.
What is rheumatism?
When it comes to 'rheumatism,' we often think of arthritis.
However, 'rheumatism', derived from the ancient Greek word 'rheuma', which means 'things of flowing nature', or circulation of bad body fluids, includes all diseases caused by abnormalities in the immune system of the blood flowing throughout the body. It is known that there are more than 200 types of rheumatic diseases, many of which cause joint pain. Therefore, when a patient visits for arthritis, inquiries on the patient's various symptoms and physical examination are necessary to identify the type of rheumatism.
Main symptoms of rheumatism
- 1Chronic fatigue
- 2Old fever with no cause
- 3Cold hands and feet, or skin color changes in places with low temperatures
- 4Multiple joint pain rash in knee, wrist, finger, shoulder, neck, waist, ankle, etc.
- 5Stiffness of the joints when waking up from sleep
- 6Frequent canker sore or dry mouth or eyes
- 7Red rash around the cheeks, disc-shaped skin rash, or purplish on extremities
Typical rheumatoid diseases
-
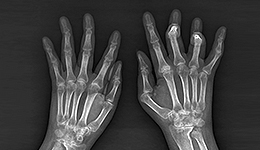
Rheumatoid arthritis A joint is a place where bones meet with each other and it is surrounded by a thin synovial membrane that produces joint fluid (synovial fluid). Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory systemic disease characterized by a persistent inflammatory response of the joint synovial membrane. The main clinical feature is that the damage of the joint cartilage and bone erosion occur due to the continuous chronic inflammatory reaction of the synovial membrane, resulting in the destruction of the joint and malfunction.
-
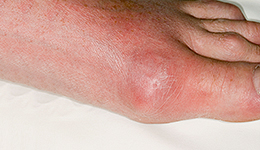
Gout Gout is a disease that occurs when uric acid in a person's blood rises excessively to form crystals, to which inflammatory reaction causes severe joint pain. With the improvement of eating habits, the incidence of gout is also increasing in Korea, and it is one of the most common causes of inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40. Along with the acute pain, the joint swells and reddens, and the pain is too severe to touch. The most common site is the big toe, but it is also common on the instep, heel, ankle, and knee. Since it is due to the elevated uric acid, drug therapy and diet must be steadily implemented to lower uric acid.
-

Ankylsoing spondylitis Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of chronic arthritis characterized by major lesions of the spine. ‘Ankylosing’ means ‘stiffening’ or ‘hardening’, and spondylitis literally means ‘inflammation of the spine’. In addition to the spine, it can also cause inflammation in joints such as the hip, knee, and shoulder. Ankylosing spondylitis can vary from mild to very severe. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can control pain or stiffness, which can reduce or prevent the occurrence of severe deformities.
-
Behcet's disease Behcet's disease, an autoimmune disease, is characterized by mouth ulcers. In addition, it is one of the chronic inflammatory recurrent diseases that are accompanied by a combination of vulvar ulcers, ocular symptoms, skin symptoms, and symptoms of joints and organs. To date, the cause of Behcet's disease has not been clearly identified, but various inflammatory symptoms are known to occur as a result of problems with the immune function due to genetic and environmental factors.
-

Lupus The correct name for lupus is systemic lupus erythematosus, and it is a chronic autoimmune disease that mainly occurs at a young age, including women of childbearing age. Diagnosis is difficult because symptoms vary from patient to patient and develop slowly over weeks to years. In general, systemic fatigue, muscle pain, mild or high fever, weight loss, and hair loss are common in the early stages. Also, a butterfly-shaped skin rash occurs on both cheeks, or the joint is swollen and painful.
Diagnosis of rheumatism
Usually, medical history and physical examination can result in a diagnosis. Blood tests may be needed to check for rheumatoid factors and severity of inflammation, and simple radiographs of the affected joint are taken to determine the extent of the damage.
Rheumatoid immunoserologic test
Rheumatoid immunoserologic test can help predict the prognosis and classify subtypes of rheumatoid disease. Even if autoantibody turns out positive, there is no absolute meaning in it, and an accurate interpretation using the patient's clinical symptoms and other tests is needed.
| Rheumatoid factor test | The rheumatoid factor test is used when polyarthritis is suspected to be rheumatoid arthritis, but a positive result of the test does not necessarily mean rheumatoid arthritis. |
|---|---|
| Anti-CCP Antibody Test | This is to measure the antibody concentration against cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP). It is helpful in predicting future disease activity in patients with early-stage rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, it is used to screen rheumatoid arthritis patients for whom no rheumatoid factor has been found. |
| Antinuclear antibody test (ANA, FANA) | This test checks the presence of autoantibodies against cell nuclei in the serum and is used to diagnose autoimmune diseases including lupus. If the anti-nuclear antibody test is positive, additional tests are performed, such as anti-DNA antibody test, serum complement test, extractable nuclear antigen test, and anti-phospholipid antibody. |
| Anti-DNA antibody test | It is an antibody against our body's DNA and an indicator of the possibility of lupus and activity of the disease. It is used as data for evaluating the response to treatment. |
| Extractable nuclear antigen test | The extractable nuclear antigen test is used in screening several autoimmune diseases. In addition, this is done when the antinuclear antibody test is positive, and if the Sm is high at this time, it can be judged that it has high specificity for lupus. |
| Anti-cardiolipin antibody test | It is used as data to check if there is comorbidity with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and if blood clotting disorder are present. |
Rheumatism treatment

Depending on the patient’s health, different drugs are prescribed. Generally, only nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs are used if symptoms are mild. However, if there is a severe symptom and a high risk of permanent joint damage, drugs that slow the progression of the disease (anti-rheumatic drugs) are prescribed and these drugs must be taken for several months for the effects to appear. Initially, antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine or hydroxychloroquine are used.
If symptoms persist, drugs such as gold, penicillamine, methotrexate, or cyclosporine are used. These drugs can sometimes cause side effects such as kidney damage or blood disease, so careful observation is needed.
In addition, if surgery is needed, treatment is carried out in cooperation with an orthopedic surgeon, and physical therapy and exercise therapy are performed to promote physical functions.